Are you looking for 'traffic assignment methods'? You will find the answers here.
1 Introduction All-or-nothing naming. ... Incremental appointment. ... Capacity simplicity assignment. ... Drug user equilibrium assignment (UE) The user equipoise assignment is founded on Wardrop's ordinal principle, which states that no device driver can unilaterally cut his/her travel costs by shifting to another ...
Table of contents
- Traffic assignment methods in 2021
- Traffic assignment pdf
- Traffic assignment example
- All-or-nothing traffic assignment
- Types of traffic assignment
- Capacity restraint traffic assignment
- What is traffic assignment
- Research methods assignment
Traffic assignment methods in 2021
 This picture representes traffic assignment methods.
This picture representes traffic assignment methods.
Traffic assignment pdf
 This image illustrates Traffic assignment pdf.
This image illustrates Traffic assignment pdf.
Traffic assignment example
 This picture demonstrates Traffic assignment example.
This picture demonstrates Traffic assignment example.
All-or-nothing traffic assignment
 This picture illustrates All-or-nothing traffic assignment.
This picture illustrates All-or-nothing traffic assignment.
Types of traffic assignment
 This image shows Types of traffic assignment.
This image shows Types of traffic assignment.
Capacity restraint traffic assignment
 This picture demonstrates Capacity restraint traffic assignment.
This picture demonstrates Capacity restraint traffic assignment.
What is traffic assignment
 This image illustrates What is traffic assignment.
This image illustrates What is traffic assignment.
Research methods assignment
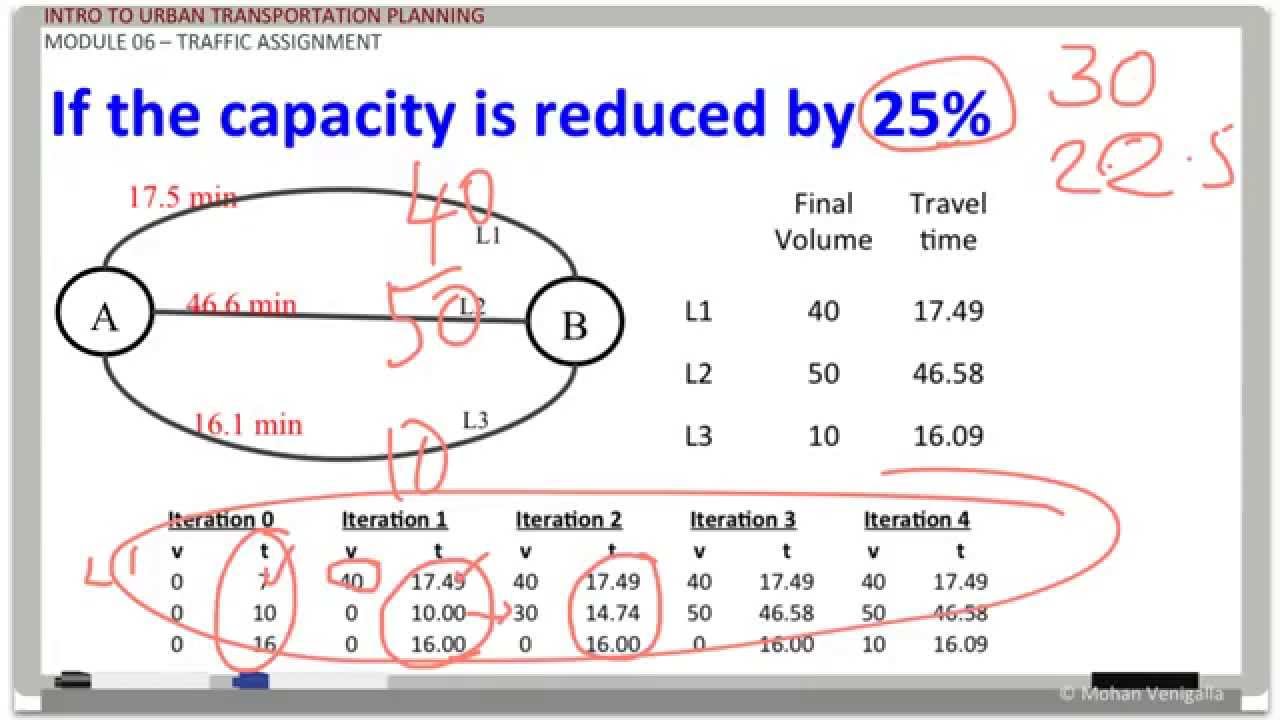 This picture illustrates Research methods assignment.
This picture illustrates Research methods assignment.
What are the different types of traffic assignment?
The types of traffic assignment models are all-or-nothing assignment, incremental assignment, capacity restraint assignment, user equilibrium assignment (UE), stochastic user equilibrium assignment (SUE), system optimum assignment (SO), etc.
How does incremental assignment work in traffic management?
Incremental assignment is a process in which fractions of traffic volumes are assigned in steps.In each step, a fixed proportion of total demand is assigned, based on all-or-nothing assignment. After each step, link travel times are recalculated based on link volumes.
What do you need to know about route assignment?
To determine facility needs and costs and benefits, we need to know the number of travelers on each route and link of the network (a route is simply a chain of links between an origin and destination). We need to undertake traffic (or trip) assignment.
Why is the UE problem of traffic assignment convex?
All other routes have either equal or heavy travel times. The user equilibrium criteria is thus met for every O-D pair. The UE problem is convex because the link travel time functions are monotonically increasing function, and the link travel time a particular link is independent of the flow and other links of the networks.
Last Update: Oct 2021