Are you having trouble finding 'alpha process nucleosynthesis'? All the details can be found here.
Fusing with additional He nuclei can make over heavier elements stylish a chain of stellar nucleosynthesis noted as the explorative process, but these reactions are exclusive significant at high temperatures and pressures than in cores undergoing the triple-alpha process.
Table of contents
- Alpha process nucleosynthesis in 2021
- In which of the following nucleus does the alpha process end?
- Process by which elements are created within the star
- Triple alpha process equation
- Supernova nucleosynthesis
- Helium fusion in stars
- The triple-alpha process quizlet
- Alpha ladder nucleosynthesis
Alpha process nucleosynthesis in 2021
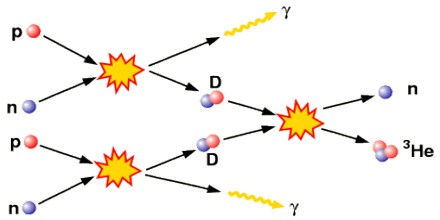 This image demonstrates alpha process nucleosynthesis.
This image demonstrates alpha process nucleosynthesis.
In which of the following nucleus does the alpha process end?
 This picture illustrates In which of the following nucleus does the alpha process end?.
This picture illustrates In which of the following nucleus does the alpha process end?.
Process by which elements are created within the star
 This picture demonstrates Process by which elements are created within the star.
This picture demonstrates Process by which elements are created within the star.
Triple alpha process equation
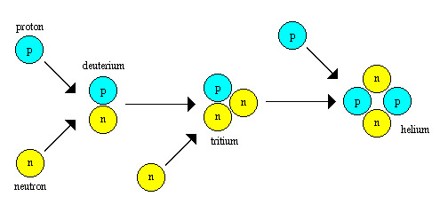 This picture representes Triple alpha process equation.
This picture representes Triple alpha process equation.
Supernova nucleosynthesis
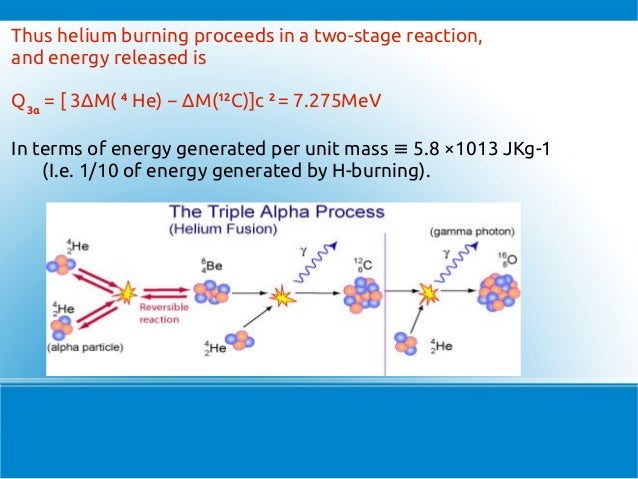 This image shows Supernova nucleosynthesis.
This image shows Supernova nucleosynthesis.
Helium fusion in stars
 This picture representes Helium fusion in stars.
This picture representes Helium fusion in stars.
The triple-alpha process quizlet
 This image demonstrates The triple-alpha process quizlet.
This image demonstrates The triple-alpha process quizlet.
Alpha ladder nucleosynthesis
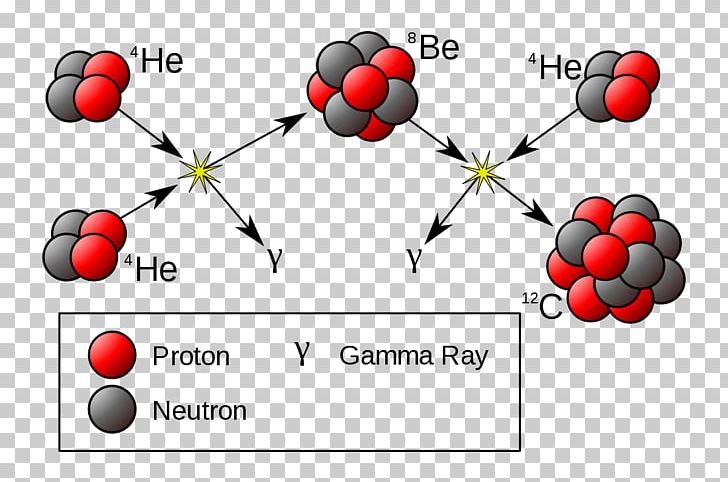 This picture shows Alpha ladder nucleosynthesis.
This picture shows Alpha ladder nucleosynthesis.
How is stable carbon formed in nucleosynthesis?
Two helium nuclei ("alpha particles") fuse to form unstable beryllium. If another helium nucleus can fuse with the beryllium nucleus before it decays, stable carbon is formed along with a gamma ray. How does this depend on temperature?
How does the process of nucleosynthesis create new nuclei?
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons (protons and neutrons).
Why is nucleosynthesis called the triple alpha process?
But there is always a small amount of 8 4 Be at any moment that is available to fuse with a third helium to produce 12 6 C. This improbable sequence is called the triple-alpha process because the net effect is to combine 3 alpha particles to form a 12 6 C nucleus.
Where does helium come from in the triple alpha process?
The triple-alpha process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions by which three helium-4 nuclei ( alpha particles) are transformed into carbon. Helium accumulates in the cores of stars as a result of the proton–proton chain reaction and the carbon–nitrogen–oxygen cycle .
Last Update: Oct 2021